本篇初步探索了xgboost在调参数的方法
背景:数据科学里,首先要对数据特征的提取建模,然后用机器学习模拟预测。目前来说,工业界暂时不清楚,但是在只要涉及数据科学的比赛,机器学习模型肯定少补了Xgboost。Xgboost的参数非常繁多(50多个参数),本次主要介绍如何进行Xgboost调参
调参原理:
1、利用sklearn的网格搜索GridSearchCV进行调试,但是GridSearchCV无法直接对xgboost进行调试 2、利用xgboost的sklearn接口XGBRegressor/XGBClassifier,利用接口,将xgboost的参数带入到GridSearchCV进行遍历调优
调参原则:
1、参数先粗调再微调 2、参数先调对结果影响大的(哪些影响大,可以上网先找找) 3、分批次调参
Xgboost的参数
- General parameters relates to which booster we are using to do boosting, commonly tree or linear model
- Booster parameters depends on which booster you have chosen
- Learning Task parameters that decides on the learning scenario, for example, regression tasks may use different parameters with ranking tasks.
- Command line parameters that relates to behavior of CLI version of xgboost.
调参的顺序:
1、选定一组基准参数,这些参数有经验的话,用经验值,没有经验可以用官方的默认值 2 、max_depth 和 min_child_weight 参数调优 3、gamma参数调优 4、调整subsample 和 colsample_bytree 参数调优 5、正则化参数调优(reg_alpha、reg_lambda 6、降低学习率和使用更多的树(learning_rate、n_estimators) 7、可以探索的参数max_delta_step 、scale_pos_weight、base_score
接下来让我们先导入对应的模块,且对数据进行一定的处理
#Import libraries:
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import xgboost as xgb
from xgboost.sklearn import XGBRegressor
from sklearn import cross_validation, metrics #Additional scklearn functions
from sklearn.grid_search import GridSearchCV #Perforing grid search
import matplotlib.pylab as plt
#import warnings
#warnings.filterwarnings('ignore')
%matplotlib inline
from matplotlib.pylab import rcParams
rcParams['figure.figsize'] = 12, 4
from sklearn.metrics import mean_absolute_error
from sklearn.metrics import fbeta_score, make_scorer
from sklearn.metrics import mean_squared_error
from math import sqrt
train = pd.read_csv('../../raw/LiChuan/trainSaleDate.csv')
# 去掉 2012 年数据, 噪音太多
train = train.drop(train['year']==2012)
train.drop_duplicates(inplace=True)
labels = train.sale_quantity
train = train.drop(['class_id','sale_quantity', 'sale_date'], axis=1)
# train_test = pd.concat([train, test]).reset_index(drop=True)
year_dummies = pd.get_dummies(train['year'], prefix='year')
month_dummies = pd.get_dummies(train['month'], prefix='month')
train = pd.concat([train, year_dummies], axis=1)
train = pd.concat([train, month_dummies], axis=1)
train = train.drop(['year', 'month'], axis=1)
train.fillna(0.0, inplace=True)
# 获取 2017-10 数据作为测试集
test_X = train[-140:]
test_Y = labels[-140:]
# 2012-01 至 2017-10 作为训练集
train_X = train[:-140]
train_Y = labels[:-140]
def modelfit(alg,useTrainCV=True, cv_folds=5, early_stopping_rounds=50):
if useTrainCV:
xgb_param = alg.get_xgb_params()
xgtrain =xgb.DMatrix(train_X,label=train_Y)
xgtest = xgb.DMatrix(test_X)
cvresult = xgb.cv(xgb_param, xgtrain, num_boost_round=alg.get_params()['n_estimators'], nfold=cv_folds,
early_stopping_rounds=early_stopping_rounds,show_stdv=False)
alg.set_params(n_estimators=cvresult.shape[0])#cvresult.shape[0]和alg.get_params()['n_estimators']值一样
#Fit the algorithm on the data
alg.fit(train_X, train_Y,eval_metric='rmse')
#Predict training set:
dtrain_predictions = alg.predict(train_X)
#Print model report:
print(" Score (Train): %f" % metrics.mean_squared_error(train_Y.values, dtrain_predictions))
#Predict on testing data:
dtest_predictions = alg.predict(test_X)
print("Score (Test): %f" % metrics.mean_squared_error(test_Y.values, dtest_predictions))
1、选定一组基准参数,这些参数有经验的话,用经验值,没有经验可以用官方的默认值
xgb1 = XGBRegressor(booster='gbtree',
objective= 'reg:linear',
eval_metric='rmse',
gamma = 0.1,
min_child_weight= 1.1,
max_depth= 5,
subsample= 0.8,
colsample_bytree= 0.8,
tree_method= 'exact',
learning_rate=0.1,
n_estimators=100,
nthread=4,
scale_pos_weight=1,
seed=27)
modelfit(xgb1)
Score (Train): 8054.387826
Score (Test): 27418.413465
xgb1的参数
base_score=0.5, booster=’gbtree’, colsample_bylevel=1, colsample_bytree=0.8, eval_metric=’rmse’, gamma=0.1, learning_rate=0.1, max_delta_step=0, max_depth=5, min_child_weight=1.1, missing=None, n_estimators=400, n_jobs=1, nthread=4, objective=’reg:linear’, random_state=0, reg_alpha=0, reg_lambda=1, scale_pos_weight=1, seed=27, silent=True, subsample=0.8, tree_method=’exact’
2、 max_depth 和 min_child_weight 参数调优
%%time
#Grid seach on subsample and max_features
#Choose all predictors except target & IDcols
param_test1 = {
'max_depth':[3,5,7,9],
'min_child_weight':[1,3,5]
}
gsearch1 = GridSearchCV(estimator = XGBRegressor(booster='gbtree',
objective= 'reg:linear',
eval_metric='rmse',
gamma = 0.1,
min_child_weight= 1.1,
max_depth= 5,
subsample= 0.8,
colsample_bytree= 0.8,
tree_method= 'exact',
learning_rate=0.1,
n_estimators=100,
nthread=4,
scale_pos_weight=1,
seed=27),
param_grid = param_test1, scoring='mean_squared_error',n_jobs=4,iid=False, cv=5)
gsearch1.fit(train_X,train_Y)
CPU times: user 8.41 s, sys: 323 ms, total: 8.73 s Wall time: 1min 50s
gsearch1.grid_scores_, gsearch1.best_params_, gsearch1.best_score_
([mean: -37307.30173, std: 20190.10346, params: {‘max_depth’: 3, ‘min_child_weight’: 1}, mean: -37858.56838, std: 20117.31618, params: {‘max_depth’: 3, ‘min_child_weight’: 3}, mean: -37074.47698, std: 18889.70050, params: {‘max_depth’: 3, ‘min_child_weight’: 5}, mean: -33870.23259, std: 19987.57504, params: {‘max_depth’: 5, ‘min_child_weight’: 1}, mean: -33240.71438, std: 18837.21289, params: {‘max_depth’: 5, ‘min_child_weight’: 3}, mean: -36997.23968, std: 22463.08107, params: {‘max_depth’: 5, ‘min_child_weight’: 5}, mean: -33965.78497, std: 18547.66643, params: {‘max_depth’: 7, ‘min_child_weight’: 1}, mean: -34735.79444, std: 20149.70986, params: {‘max_depth’: 7, ‘min_child_weight’: 3}, mean: -37111.82576, std: 22824.75284, params: {‘max_depth’: 7, ‘min_child_weight’: 5}, mean: -35508.45759, std: 19274.54528, params: {‘max_depth’: 9, ‘min_child_weight’: 1}, mean: -35914.95148, std: 20508.98895, params: {‘max_depth’: 9, ‘min_child_weight’: 3}, mean: -36943.84821, std: 20971.33128, params: {‘max_depth’: 9, ‘min_child_weight’: 5}], {‘max_depth’: 5, ‘min_child_weight’: 3}, -33240.714381367696)
不放心的话尝试一下其他值
%%time
#Grid seach on subsample and max_features
#Choose all predictors except target & IDcols
param_test1b = {
'min_child_weight':[6,8,10,12]
}
gsearch1b = GridSearchCV(estimator = XGBRegressor(booster='gbtree',
objective= 'reg:linear',
eval_metric='rmse',
gamma = 0.1,
min_child_weight= 1.1,
max_depth= 5,
subsample= 0.8,
colsample_bytree= 0.8,
tree_method= 'exact',
learning_rate=0.1,
n_estimators=100,
nthread=4,
scale_pos_weight=1,
seed=27),
param_grid = param_test1b, scoring='mean_squared_error',n_jobs=4,iid=False, cv=5)
gsearch1b.fit(train_X,train_Y)
CPU times: user 7.28 s, sys: 187 ms, total: 7.46 s Wall time: 36.1 s
gsearch1b.grid_scores_, gsearch1b.best_params_, gsearch1b.best_score_
([mean: -37171.16050, std: 21067.04892, params: {‘min_child_weight’: 6}, mean: -36495.04327, std: 20191.87333, params: {‘min_child_weight’: 8}, mean: -36298.35708, std: 19605.68520, params: {‘min_child_weight’: 10}, mean: -35836.89718, std: 18897.25594, params: {‘min_child_weight’: 12}], {‘min_child_weight’: 12}, -35836.89718422033)
3、gamma参数调优
%%time
param_test3 = {
'gamma':[i/10.0 for i in range(0,5)]
}
gsearch3 = GridSearchCV(estimator = XGBRegressor(booster='gbtree',
objective= 'reg:linear',
eval_metric='rmse',
gamma = 0.1,
min_child_weight= 3,
max_depth= 5,
subsample= 0.8,
colsample_bytree= 0.8,
tree_method= 'exact',
learning_rate=0.1,
n_estimators=100,
nthread=4,
scale_pos_weight=1,
seed=27),
param_grid = param_test3, scoring='mean_squared_error',n_jobs=4,iid=False, cv=5)
gsearch3.fit(train_X,train_Y)
CPU times: user 7.82 s, sys: 227 ms, total: 8.05 s Wall time: 48.6 s
gsearch3.grid_scores_, gsearch3.best_params_, gsearch3.best_score_
([mean: -33240.71438, std: 18837.21289, params: {‘gamma’: 0.0}, mean: -33240.71438, std: 18837.21289, params: {‘gamma’: 0.1}, mean: -33240.71438, std: 18837.21289, params: {‘gamma’: 0.2}, mean: -33240.71438, std: 18837.21289, params: {‘gamma’: 0.3}, mean: -33240.71438, std: 18837.21289, params: {‘gamma’: 0.4}], {‘gamma’: 0.0}, -33240.714381367696)
4、调整subsample 和 colsample_bytree 参数调优
%%time
#Grid seach on subsample and max_features
#Choose all predictors except target & IDcols
param_test4 = {
'subsample':[i/10.0 for i in range(6,10)],
'colsample_bytree':[i/10.0 for i in range(6,10)]
}
gsearch4 = GridSearchCV(estimator = XGBRegressor(booster='gbtree',
objective= 'reg:linear',
eval_metric='rmse',
gamma = 0.1,
min_child_weight= 3,
max_depth= 5,
subsample= 0.8,
colsample_bytree= 0.8,
tree_method= 'exact',
learning_rate=0.1,
n_estimators=100,
nthread=4,
scale_pos_weight=1,
seed=27),
param_grid = param_test4, scoring='mean_squared_error',n_jobs=4,iid=False, cv=5)
gsearch4.fit(train_X,train_Y)
CPU times: user 9.08 s, sys: 409 ms, total: 9.49 s Wall time: 1min 56s
gsearch4.grid_scores_, gsearch4.best_params_, gsearch4.best_score_
([mean: -33599.72943, std: 18191.85111, params: {‘colsample_bytree’: 0.6, ‘subsample’: 0.6}, mean: -34504.14133, std: 18332.87810, params: {‘colsample_bytree’: 0.6, ‘subsample’: 0.7}, mean: -34742.90855, std: 20106.86473, params: {‘colsample_bytree’: 0.6, ‘subsample’: 0.8}, mean: -34180.71176, std: 21119.88727, params: {‘colsample_bytree’: 0.6, ‘subsample’: 0.9}, mean: -33706.05489, std: 17873.54056, params: {‘colsample_bytree’: 0.7, ‘subsample’: 0.6}, mean: -35365.73247, std: 20734.72408, params: {‘colsample_bytree’: 0.7, ‘subsample’: 0.7}, mean: -36003.56230, std: 20460.12605, params: {‘colsample_bytree’: 0.7, ‘subsample’: 0.8}, mean: -35102.41564, std: 20596.99663, params: {‘colsample_bytree’: 0.7, ‘subsample’: 0.9}, mean: -34071.12767, std: 18824.45763, params: {‘colsample_bytree’: 0.8, ‘subsample’: 0.6}, mean: -34306.79986, std: 18037.63492, params: {‘colsample_bytree’: 0.8, ‘subsample’: 0.7}, mean: -33240.71438, std: 18837.21289, params: {‘colsample_bytree’: 0.8, ‘subsample’: 0.8}, mean: -34715.48443, std: 20364.52260, params: {‘colsample_bytree’: 0.8, ‘subsample’: 0.9}, mean: -33987.86273, std: 19097.36063, params: {‘colsample_bytree’: 0.9, ‘subsample’: 0.6}, mean: -36383.21876, std: 19792.39516, params: {‘colsample_bytree’: 0.9, ‘subsample’: 0.7}, mean: -33689.36936, std: 18809.76111, params: {‘colsample_bytree’: 0.9, ‘subsample’: 0.8}, mean: -35748.16003, std: 21143.52892, params: {‘colsample_bytree’: 0.9, ‘subsample’: 0.9}], {‘colsample_bytree’: 0.8, ‘subsample’: 0.8}, -33240.714381367696)
5、正则化参数调优(reg_alpha、reg_lambda)
粗调
%%time
#Grid seach on subsample and max_features
#Choose all predictors except target & IDcols
param_test6 = {
'reg_alpha':[1e-5, 1e-2, 0.1, 1, 100]
}
gsearch6 = GridSearchCV(estimator = XGBRegressor(booster='gbtree',
objective= 'reg:linear',
eval_metric='rmse',
gamma = 0.1,
min_child_weight= 3,
max_depth= 5,
subsample= 0.8,
colsample_bytree= 0.8,
tree_method= 'exact',
learning_rate=0.1,
n_estimators=100,
nthread=4,
scale_pos_weight=1,
seed=27),
param_grid = param_test6, scoring='mean_squared_error',n_jobs=4,iid=False, cv=5)
gsearch6.fit(train_X,train_Y)
CPU times: user 7.53 s, sys: 202 ms, total: 7.73 s Wall time: 46.5 s
gsearch6.grid_scores_, gsearch6.best_params_, gsearch6.best_score_
([mean: -33240.71449, std: 18837.21316, params: {‘reg_alpha’: 1e-05}, mean: -33240.70394, std: 18837.19242, params: {‘reg_alpha’: 0.01}, mean: -33240.61475, std: 18837.01487, params: {‘reg_alpha’: 0.1}, mean: -33655.05163, std: 19188.16195, params: {‘reg_alpha’: 1}, mean: -33518.91580, std: 19324.08680, params: {‘reg_alpha’: 100}], {‘reg_alpha’: 0.1}, -33240.6147525903)
微调
%%time
#Grid seach on subsample and max_features
#Choose all predictors except target & IDcols
param_test7 = {
'reg_alpha':[0, 0.001, 0.005, 0.01, 0.05]
}
gsearch7 = GridSearchCV(estimator = XGBRegressor(booster='gbtree',
objective= 'reg:linear',
eval_metric='rmse',
gamma = 0.1,
min_child_weight= 3,
max_depth= 5,
subsample= 0.8,
colsample_bytree= 0.8,
tree_method= 'exact',
learning_rate=0.1,
n_estimators=100,
nthread=4,
scale_pos_weight=1,
seed=27),
param_grid = param_test7, scoring='mean_squared_error',n_jobs=4,iid=False, cv=5)
gsearch7.fit(train_X,train_Y)
CPU times: user 7.49 s, sys: 199 ms, total: 7.69 s Wall time: 46.2 s
gsearch7.grid_scores_, gsearch7.best_params_, gsearch7.best_score_
([mean: -33240.71438, std: 18837.21289, params: {‘reg_alpha’: 0}, mean: -33240.71515, std: 18837.21306, params: {‘reg_alpha’: 0.001}, mean: -33240.71029, std: 18837.20469, params: {‘reg_alpha’: 0.005}, mean: -33240.70394, std: 18837.19242, params: {‘reg_alpha’: 0.01}, mean: -33240.66275, std: 18837.11462, params: {‘reg_alpha’: 0.05}], {‘reg_alpha’: 0.05}, -33240.66275176923)
6、降低学习率和使用更多的树(learning_rate、n_estimators)
%%time
#Grid seach on subsample and max_features
#Choose all predictors except target & IDcols
param_test9 = {
'n_estimators':[50, 100, 200, 500,1000],
'learning_rate':[0.001, 0.01, 0.05, 0.1,0.2]
}
gsearch9 = GridSearchCV(estimator = XGBRegressor(booster='gbtree',
objective= 'reg:linear',
eval_metric='rmse',
gamma = 0.1,
min_child_weight= 3,
max_depth= 5,
subsample= 0.8,
colsample_bytree= 0.8,
tree_method= 'exact',
learning_rate=0.1,
n_estimators=100,
nthread=4,
scale_pos_weight=1,
reg_alpha=0.05,
seed=27),
param_grid = param_test9, scoring='mean_squared_error',n_jobs=4,iid=False, cv=5)
gsearch9.fit(train_X,train_Y)
CPU times: user 18 s, sys: 400 ms, total: 18.4 s Wall time: 11min 48s
gsearch9.grid_scores_, gsearch9.best_params_, gsearch9.best_score_
([mean: -269735.38582, std: 100248.84349, params: {‘learning_rate’: 0.001, ‘n_estimators’: 50}, mean: -248451.90827, std: 91899.96797, params: {‘learning_rate’: 0.001, ‘n_estimators’: 100}, mean: -211548.39700, std: 76958.64307, params: {‘learning_rate’: 0.001, ‘n_estimators’: 200}, mean: -134974.04245, std: 47851.47997, params: {‘learning_rate’: 0.001, ‘n_estimators’: 500}, mean: -73521.66556, std: 25935.98271, params: {‘learning_rate’: 0.001, ‘n_estimators’: 1000}, mean: -134499.16558, std: 47613.16020, params: {‘learning_rate’: 0.01, ‘n_estimators’: 50}, mean: -72947.14830, std: 26031.50160, params: {‘learning_rate’: 0.01, ‘n_estimators’: 100}, mean: -39440.09082, std: 16239.31453, params: {‘learning_rate’: 0.01, ‘n_estimators’: 200}, mean: -33312.98785, std: 18013.88261, params: {‘learning_rate’: 0.01, ‘n_estimators’: 500}, mean: -33663.99313, std: 20179.74172, params: {‘learning_rate’: 0.01, ‘n_estimators’: 1000}, mean: -36502.96591, std: 16225.13167, params: {‘learning_rate’: 0.05, ‘n_estimators’: 50}, mean: -33665.06976, std: 18138.93215, params: {‘learning_rate’: 0.05, ‘n_estimators’: 100}, mean: -34120.16927, std: 20085.98727, params: {‘learning_rate’: 0.05, ‘n_estimators’: 200}, mean: -34177.57983, std: 21188.62796, params: {‘learning_rate’: 0.05, ‘n_estimators’: 500}, mean: -34660.48776, std: 22025.55298, params: {‘learning_rate’: 0.05, ‘n_estimators’: 1000}, mean: -33838.33799, std: 17860.13547, params: {‘learning_rate’: 0.1, ‘n_estimators’: 50}, mean: -33240.66275, std: 18837.11462, params: {‘learning_rate’: 0.1, ‘n_estimators’: 100}, mean: -33181.90461, std: 19910.96435, params: {‘learning_rate’: 0.1, ‘n_estimators’: 200}, mean: -33576.53561, std: 20349.66997, params: {‘learning_rate’: 0.1, ‘n_estimators’: 500}, mean: -34053.72276, std: 20703.38247, params: {‘learning_rate’: 0.1, ‘n_estimators’: 1000}, mean: -35845.98638, std: 21392.95943, params: {‘learning_rate’: 0.2, ‘n_estimators’: 50}, mean: -35973.28358, std: 22094.74565, params: {‘learning_rate’: 0.2, ‘n_estimators’: 100}, mean: -36080.64404, std: 22257.37518, params: {‘learning_rate’: 0.2, ‘n_estimators’: 200}, mean: -36633.99577, std: 22674.09668, params: {‘learning_rate’: 0.2, ‘n_estimators’: 500}, mean: -36964.93338, std: 22742.96590, params: {‘learning_rate’: 0.2, ‘n_estimators’: 1000}], {‘learning_rate’: 0.1, ‘n_estimators’: 200}, -33181.904612290644)
注意
调完参数之后有两种方式进行使用xgboost
1、直接用接口XGBRegressor,fit之后在预测。好处:快,运行的后的效果还可以
2、用xgboost先训练,再预测。好处:鲁棒性比较高
首先将之前调完的参数,设置好
xgb9 = XGBRegressor(booster='gbtree',
objective= 'reg:linear',
eval_metric='rmse',
gamma = 0.1,
min_child_weight= 3,
max_depth= 5,
subsample= 0.8,
colsample_bytree= 0.8,
tree_method= 'exact',
learning_rate=0.1,
n_estimators=200,
nthread=4,
scale_pos_weight=1,
reg_alpha=0.05,
seed=27)
第一种方案fit之后,在predict预测
xgb9.fit(train_X,train_Y)
XGBRegressor(base_score=0.5, booster='gbtree', colsample_bylevel=1,
colsample_bytree=0.8, eval_metric='rmse', gamma=0.1,
learning_rate=0.1, max_delta_step=0, max_depth=5,
min_child_weight=3, missing=None, n_estimators=200, n_jobs=1,
nthread=4, objective='reg:linear', random_state=0, reg_alpha=0.05,
reg_lambda=1, scale_pos_weight=1, seed=27, silent=True,
subsample=0.8, tree_method='exact')
sqrt(mean_squared_error(xgb9.predict(test_X),test_Y))
163.93821478808687
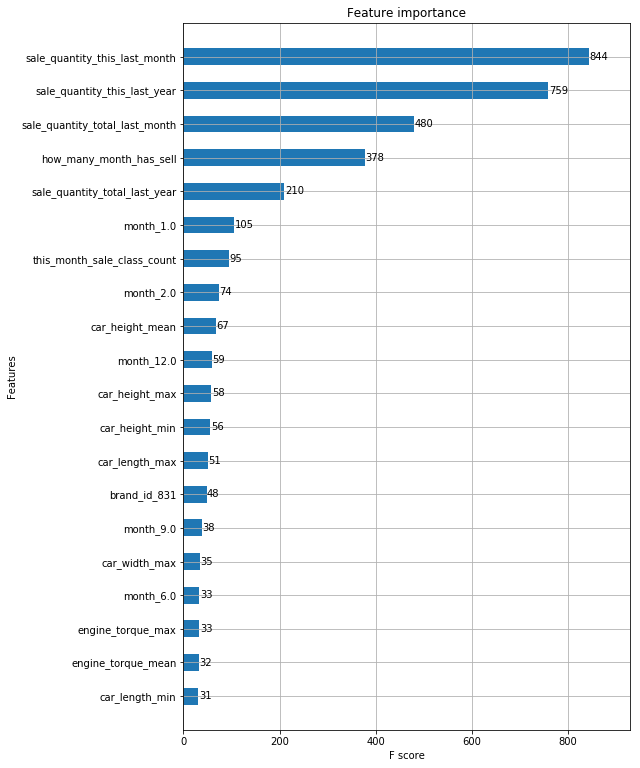
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 1, figsize=(8, 13))
xgb.plot_importance(xgb9, max_num_features=20, height=0.5, ax=ax)
trainset = xgb.DMatrix(train_X,label=train_Y)
testset = xgb.DMatrix(test_X)
第二种:train完之后在predict
%%time
model=xgb.train(xgb9.get_params(),trainset,num_boost_round=10000,evals=watchlist)
[0] train-rmse:494.438 [1] train-rmse:453.211 [2] train-rmse:415.193 [3] train-rmse:381.363 [4] train-rmse:353.229 … [9996] train-rmse:0.43133 [9997] train-rmse:0.431213 [9998] train-rmse:0.431125 [9999] train-rmse:0.431063 CPU times: user 12min 15s, sys: 4.81 s, total: 12min 20s Wall time: 12min 19s
test_predict=model.predict(testset)
rmse_test_10=sqrt(mean_squared_error(test_predict,test_Y))
rmse_test_10
168.7448358242037
注意;这里看着第一种方案比第二种方案似乎表现更好一些,但是如果我们拿到线上去测试,会发现第一种方案实际效果差很多。
初步原因
上图树图是fit 下图树图是train,初步观察到:两个图在前三层节点都是一样的,第四和第五层train节点明显比fit要多,更茂密的树应该是鲁棒性(robust)更好一些,这一点应该是初步可以解释train比fit效果更好的原因 关于Grandient Boosting的原理可以参考这篇文章Complete Guide to Parameter Tuning in Gradient Boosting (GBM) in Python


